Integrated Science & Technology, Inc.
Corporate Headquarters
Fax: 770-425-0295
Telephone:
3301 Windy Ridge Pkwy, Ste 250, Atlanta, GA 30339
Copyright © 2016 Integrated Science & Technology, Inc. | All Rights Reserved
REMEDIATION OF SMALL ARMS FIRING RANGE
Working with ADI Corporation, Integrated Science & Technology, Inc. (IST) was engaged to evaluate the Cheatham Annex small arms firing range, Yorktown Naval Weapons Station, in Yorkstown, Virginia. Its configuration is typical of firing ranges that utilize an earthen berm backstop. IST evaluated the Cheatham Annex range using the U.S. Army Range Evaluation Software Tool (REST). The results of the REST assessment suggested that there was a strong potential for lead (Pb) corrosion, Pb particles erosion, and ground-water contamination by Pb.
Site History/Problem:
IST evaluated a number of conventional and innovative technology approaches to the environmental management and remediation of small arms firing ranges, including the use of bullet traps, soil/berm management techniques, physical separation to remove larger Pb particles, acid leaching to remediate the soil, and soil additions to remediate the soil. A technology evaluation matrix was constructed and used to compare and contrast the various technology approaches. The following criteria were used to evaluate the technologies:
1) Substantial reduction of potential environmental risk
2) Modest cost
3) The ability to use in-house forces to implement the technology
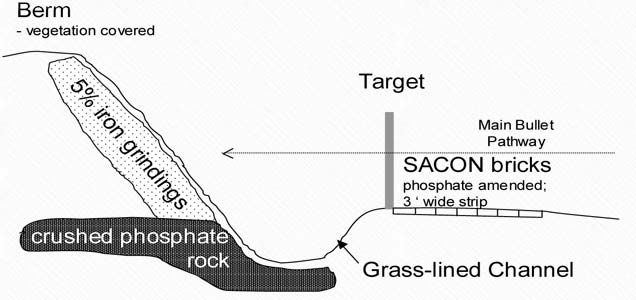
Three innovative soil/berm management technologies were selected as most appropriate for application at the Cheatham Annex small arms firing range: amendments of granular zero-valent iron (Fe0) to berm impact soil, amendments of crushed phosphate rock at the base of the firing range berm; and phosphate-amended Shock-Absorbing Concrete (SACON) blocks on the ground surface in front of the targets.
The use of these three technologies together reduces the extent of the corrosion of Pb metal bullets, immobilizes the toxic Pb corrosion products that will still inevitably form, and reduces erosion of Pb particles. These cost-effective innovative technologies should significantly reduce the environmental risk associated with small arms firing range activities and can be easily implemented using inhouse forces.
The Navy utilized the evaluation IST provided and appreciated the novel approach presented.
Additional Projects
IST's Solution:
The Success:
Schematic of innovative berm/soil management approaches: 1) iron grindings to inhibit Pb corrosion and sequester Pb+2aq on iron hydroxides (ion exchange); 2) crushed phosphate rock to immobilize Pb by formation of pyromorphites, low solubility Pb phosphate minerals; and 3) phosphate-amended SACON bricks (3-foot wide strip) in front of target.
- Evaluated Firing Range Using U.S. Army Range Evaluation Software Tool
- Identified Potential Lead Corrosion, Lead Particles Erosion, and Ground Water Contamination
- Constructed a Technology Evaluation Matrix to Compare and Contrast Approaches
- Recommended Three Innovative Soil/Berm Management Technologies